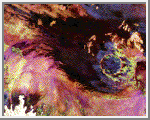
 Roter Kamm, SAR-C/X-SAR Image
Roter Kamm, SAR-C/X-SAR Image This space radar image shows the Roter Kamm impact crater. The crater rim is seen as a radar-bright, circular feature. The bright white, irregular feature in the lower left corner is a small hill of exposed rock outcrop. Roter Kamm is a moderate sized impact crater, 2.5 kilometers (1.55 miles) in diameter, and is 130 meters (427 feet) deep. However, its original floor is covered by sand deposits at least 100 meters (328 feet) thick. In a conventional aerial photograph, the brightly colored surfaces immediately surrounding the crater cannot be seen because they are covered by sand. The faint blue surfaces adjacent to the rim might indicate the presence of a layer of rocks ejected from the crater during the impact. The darkest areas are thick, windblown sand deposits which form dunes and sand sheets. The sand surface is smooth relative to the surrounding granite and limestone rock outcrops and appears dark in radar image. The green tones are related primarily to larger vegetation growing on sand soil, and the reddish tones are associated with thinly mantled limestone outcrops. (Courtesy NASA/JPL)

No comments:
Post a Comment